9 Vendor Management Best Practices for 2025 Success
- sultan mbs
- Jul 23, 2025
- 13 min read
In the bustling ecosystem of small businesses and event planning, especially within vibrant hubs like The Ten District, success hinges on strong partnerships. Effective vendor management is not just about negotiating prices; it's a strategic discipline that can make or break your projects and reputation. From sourcing unique local artisans for a festival on Jenks Main Street to securing reliable tech support for your boutique, the quality of your vendor relationships directly impacts your bottom line and customer experience. These connections are the lifeblood of your operations, influencing everything from cost efficiency and service quality to innovation and risk exposure.
This guide moves beyond generic advice to provide a clear, actionable framework of vendor management best practices tailored for a dynamic environment. We will explore nine critical strategies designed to help you build resilient partnerships, mitigate risks, and unlock new value. By implementing these techniques, you can transform your vendor interactions from simple transactions into powerful strategic alliances. This ensures your business not only functions smoothly but also thrives, creating exceptional outcomes for you and your clients. You will learn how to systematically select, manage, and develop your suppliers to gain a significant competitive advantage.
1. Master Comprehensive Vendor Due Diligence
Effective vendor management begins long before a contract is signed. Mastering comprehensive vendor due diligence is a foundational best practice that involves a systematic and thorough evaluation of potential partners. This process goes beyond surface-level impressions and sales pitches to uncover a vendor's true capabilities and potential risks. It’s about ensuring they can deliver on their promises without introducing unforeseen liabilities to your business.
For a small business or event planner in The Ten District, this means meticulously verifying a vendor's background. Imagine you're organizing a large community fair; this practice involves checking a caterer's health inspection records with the local health department or confirming a security firm's licensing and insurance are valid and sufficient for your event's scale. This proactive investigation prevents costly failures, reputational damage, and legal complications down the line.
Key Areas of Vendor Evaluation
A robust due diligence process assesses multiple facets of a vendor's operations. Key areas include:
Financial Health: Reviewing a vendor's financial stability helps ensure they won't go out of business mid-project.
Operational Stability: Assess their capacity, processes, and business continuity plans to confirm they can handle your needs.
Security & Compliance: For vendors handling data or operating on-site, verifying their security protocols and legal compliance is crucial.
Market Reputation: Look at past client reviews, testimonials, and industry standing to gauge reliability and service quality.
The following infographic illustrates the hierarchical structure of key metrics used to track the efficiency and effectiveness of a due diligence program.
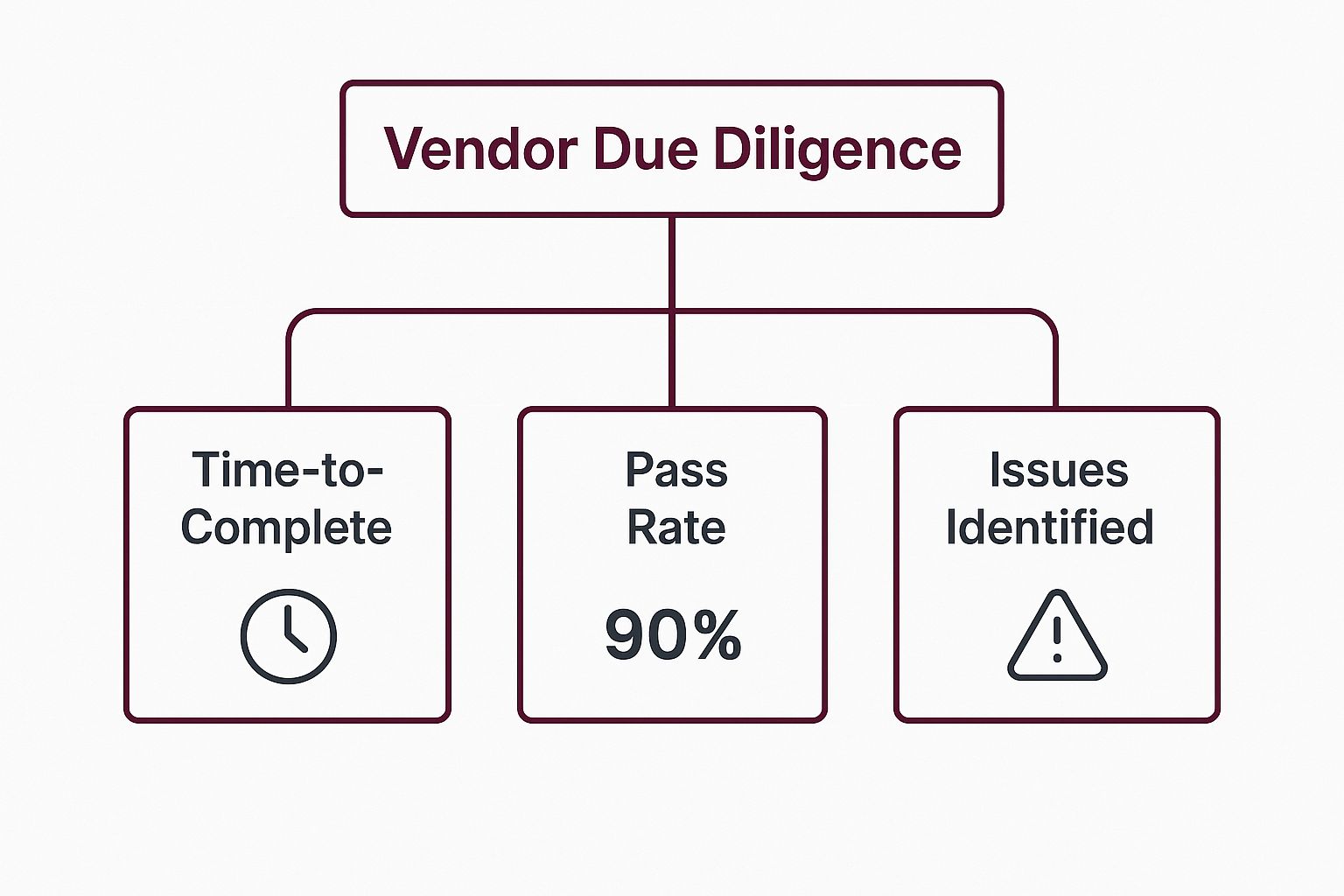
This hierarchy demonstrates how overall due diligence performance is measured by its component metrics, including completion time, success rate, and the number of issues uncovered.
2. Strategic Vendor Segmentation and Portfolio Management
Not all vendors are created equal, and they shouldn't be managed that way. One of the most effective vendor management best practices is to segment your suppliers methodically. This involves categorizing vendors based on their strategic importance, risk level, and spend volume. This allows you to apply tailored management strategies, ensuring your most critical relationships receive the attention they deserve while optimizing resources for less crucial partners.
For an event planner in The Ten District organizing a music festival, this means creating distinct vendor portfolios. Your headline act's production company is a strategic partner requiring close collaboration and daily check-ins. In contrast, the vendor supplying portable toilets is a transactional supplier, managed efficiently through clear contracts and checklists. This approach, pioneered by thinkers like Peter Kraljic, prevents you from wasting valuable time on low-impact vendors and focusing energy where it matters most.
Key Areas for Vendor Segmentation
A robust segmentation model helps allocate your management efforts effectively. Key criteria for categorization include:
Strategic Importance: How critical is the vendor to your core business or event's success? High-impact vendors, like a sole-source technology provider, require deep partnership.
Risk Level: What is the potential for business disruption if this vendor fails? Vendors handling sensitive data or providing essential infrastructure pose a higher risk.
Spend Volume: How much are you spending with this vendor? High-spend vendors often present opportunities for cost savings and negotiation.
Supplier Replaceability: How difficult would it be to replace this vendor? Unique or highly specialized suppliers demand a more collaborative management style.
By creating clear criteria for each vendor category, you can align internal resources appropriately and build stronger, more effective supplier relationships across your entire portfolio.
3. Robust Contract Management and SLA Framework
Beyond vetting vendors, the next critical step is formalizing the partnership through strong contracts and clearly defined Service Level Agreements (SLAs). This best practice involves creating a comprehensive system for developing, negotiating, monitoring, and managing vendor agreements. A robust contract management framework establishes clear expectations, defines performance standards, and provides legal protection, ensuring both parties understand their roles and responsibilities.
For a small business in The Ten District planning a recurring farmers' market, this means having an ironclad contract with the tent and stall provider. The agreement should specify exact delivery and setup times, quality standards for the equipment, and penalties for late arrival or damaged goods. This level of detail in contract management is a cornerstone of effective vendor management best practices, as it transforms verbal promises into legally enforceable commitments, safeguarding your event's success and your business's reputation.

Key Contract and SLA Components
Effective agreements are built on a foundation of specific, measurable, and relevant terms. These elements ensure accountability and provide a clear basis for performance evaluation.
Service Level Agreements (SLAs): Define the specific services to be provided and the performance levels expected. For a tech vendor, this might include uptime guarantees like Amazon Web Services' detailed SLA framework.
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs): Establish both quantitative (e.g., delivery times, response rates) and qualitative (e.g., customer satisfaction, service quality) metrics to track vendor performance.
Governance and Escalation: Outline clear procedures for regular communication, performance reviews, and how to address and resolve issues if they arise.
Flexibility and Review Clauses: Build in mechanisms that allow the contract to adapt to changing business needs and schedule regular reviews to ensure the agreement remains relevant and effective.
Adopting a systematic approach to contracts and SLAs moves relationships from handshake deals to strategic partnerships, providing a solid framework for long-term success.
4. Continuous Performance Monitoring and Scorecarding
Effective vendor management best practices extend far beyond the initial contract. Continuous performance monitoring and scorecarding involve a systematic process for tracking, measuring, and evaluating vendor performance against predefined Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) and Service Level Agreements (SLAs). This data-driven approach shifts vendor relationships from being reactive to proactive, enabling you to identify and address issues before they escalate. It fosters accountability and creates a transparent framework for continuous improvement.
For an event planner in The Ten District organizing a series of summer concerts, this means regularly tracking a sound equipment provider's on-time setup record, equipment reliability, and technical support responsiveness. Using a simple scorecard, you can quantify their performance, compare it against your standards, and have concrete data to discuss during check-ins. This ongoing evaluation ensures every concert meets the same high-quality standard, protecting your event's reputation and audience experience.
Key Actions for Implementation
To effectively monitor performance, you must translate your expectations into measurable metrics. This involves a collaborative and transparent process.
Establish Clear KPIs: Define specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) goals for each vendor. This could include delivery times, quality standards, or customer service response rates.
Develop Vendor Scorecards: Create a scorecard that tracks these KPIs. Share the results with vendors regularly to foster transparency and open dialogue about performance.
Conduct Regular Reviews: Schedule quarterly business reviews (QBRs) with key vendors to discuss scorecard results, address challenges, and plan for future improvements.
Automate Alerts: Implement systems that automatically notify you when a vendor's performance dips below a critical threshold, allowing for immediate intervention.
The following video discusses how to build and implement a successful supplier scorecarding system.
5. Integrated Risk Management and Business Continuity Planning
Beyond initial vetting, one of the most critical vendor management best practices is integrating risk management with robust business continuity planning. This involves actively identifying potential vendor-related disruptions and creating a clear plan to maintain operations if a key partner fails. It’s about anticipating challenges, from a supplier's financial collapse to a natural disaster impacting their facility, and ensuring your business can weather the storm without significant downtime or loss.
For an event planner in The Ten District organizing a major festival, this means not only having a backup power generator but also having a secondary AV equipment supplier on standby. Similarly, a local boutique relying on a single artisan for a best-selling product should cultivate relationships with other creators. This proactive approach transforms risk from a potential catastrophe into a manageable variable, safeguarding your operations and reputation.
Key Aspects of Integrated Planning
A resilient vendor ecosystem is built on foresight and preparation. Key areas of focus include:
Vendor Dependency Mapping: Visually map out your critical vendors and understand the impact their failure would have on your business.
Business Impact Analysis: Regularly assess which business functions are most vulnerable to vendor disruptions and prioritize your contingency efforts accordingly.
Contingency & Diversification: Develop alternative vendor relationships for essential services and avoid over-reliance on a single source for critical supplies or functions. Apple's famous supplier diversification strategy is a large-scale example of this principle in action.
Crisis Management Protocols: Create and test clear protocols for what to do when a vendor-related crisis occurs, ensuring a swift and effective response.
6. Cross-Functional Vendor Governance and Communication
Effective vendor management is not a siloed activity confined to a single department; it's a team sport. Adopting a cross-functional governance and communication model is one of the most impactful vendor management best practices. This approach involves creating a formal structure where stakeholders from various departments, such as procurement, legal, IT, and finance, collectively oversee vendor relationships. This ensures that vendor performance and risks are evaluated from all relevant perspectives, leading to more holistic and aligned decisions.
For an event planner in The Ten District organizing a music festival, this means forming a vendor council. This council would include the operations lead to discuss logistics with the staging company, the marketing head to coordinate with promotional partners, and the finance manager to review budgets with all suppliers. This collaborative oversight prevents critical details from slipping through the cracks and ensures every facet of the vendor relationship supports the event's overall goals.
Key Aspects of Cross-Functional Governance
A successful cross-functional framework depends on structure and clarity. Key elements to implement include:
Formal Governance Committees: Establish regular meetings with representatives from all key departments to review vendor performance, discuss challenges, and make strategic decisions.
Shared Responsibility Frameworks: Clearly define the roles, responsibilities, and decision-making authority for each department and stakeholder involved in the vendor lifecycle.
Centralized Information Hubs: Use shared platforms or databases to provide all stakeholders with access to vendor contracts, performance data, and communication logs.
Standardized Communication Protocols: Create clear guidelines for how, when, and by whom vendors should be contacted to ensure consistent messaging and avoid confusion.
By integrating diverse expertise, businesses can proactively manage risks and unlock greater value from their vendor partnerships, transforming vendor management from a simple procurement task into a strategic organizational capability.
7. Vendor Development and Strategic Partnership Building
Truly effective vendor management best practices extend beyond transactional relationships to cultivate long-term, mutually beneficial partnerships. This proactive approach involves actively investing in your key vendors to enhance their capabilities, foster innovation, and align their growth with your own strategic goals. It’s about transforming a simple supplier into a deeply integrated strategic partner who contributes significant value.
For an event planner in The Ten District organizing an annual music festival, this could mean working with a promising local sound and lighting company. Instead of just hiring them each year, you might co-invest in new, cutting-edge equipment they can use for your event and others, or provide them with detailed feedback and training opportunities to elevate their service quality. This not only guarantees you superior technical production but also helps a local business grow, strengthening the community's event ecosystem. This approach creates a powerful competitive advantage built on collaboration and shared success.
Key Areas for Strategic Partnership
Building a successful partnership program requires a focused, structured effort. Concentrate on these key areas:
Mutual Goal Setting: Establish clear, shared objectives and metrics for success. What does a successful partnership look like for both parties?
Collaborative Innovation: Create forums for joint problem-solving and brainstorming. For example, a restaurant owner might work with a local farm to cultivate unique produce specifically for their menu.
Resource and Knowledge Sharing: Provide access to training, best practices, or technology that can help your vendor improve their operations, which in turn benefits you.
Formalized Governance: Create a formal partnership agreement that outlines roles, responsibilities, communication protocols, and a clear governance structure.
Recognition and Incentives: Acknowledge and celebrate vendor achievements and innovations. This reinforces their value and motivates continued excellence.
8. Technology-Enabled Vendor Management Platforms
In today's fast-paced environment, manual vendor management can quickly become overwhelming and inefficient. Implementing technology-enabled vendor management platforms is a best practice that leverages software to automate and streamline the entire vendor lifecycle. These platforms act as a central hub for all vendor-related activities, from onboarding and contract management to performance monitoring and payment processing. This digital approach enhances efficiency, improves transparency, and provides powerful data for strategic decision-making.
For a growing small business in The Ten District, this means replacing scattered spreadsheets and email chains with a unified system. Imagine a local retailer using a platform to manage its diverse suppliers, from local artisans to national distributors. The system could automatically track contract renewal dates, monitor inventory levels from supplier data feeds, and process invoices, freeing up valuable time to focus on customer-facing activities. This strategic adoption of technology is a cornerstone of modern vendor management best practices.
Key Areas of Platform Functionality
A robust vendor management platform consolidates several critical functions into a single, integrated solution. Key areas include:
Centralized Vendor Information: A single source of truth for all vendor data, including contacts, contracts, and performance history.
Automated Onboarding and Workflow: Streamlines the process of bringing new vendors on board and automates approval workflows.
Performance Tracking and Analytics: Utilizes dashboards and analytics to monitor vendor performance against key metrics and SLAs.
Risk and Compliance Management: Helps track vendor compliance with insurance, certifications, and other regulatory requirements.
The following infographic illustrates the core components of an integrated vendor management system.
This diagram shows how different modules like procurement, risk management, and analytics connect to a central vendor database.
9. Establish a Clear Communication Protocol
Effective vendor management hinges on clear, consistent, and documented communication. Establishing a formal communication protocol is a critical best practice that eliminates ambiguity, prevents misunderstandings, and ensures all parties are aligned on expectations and progress. This framework defines how, when, and with whom information is shared, creating a single source of truth for the entire vendor relationship.
For a small business in The Ten District planning a product launch event, this means setting up a dedicated communication channel, like a shared project management board or a regular weekly check-in call with your key vendors, such as the AV technicians and venue manager. This structured approach ensures that critical details, like equipment setup times or last-minute changes to the run-of-show, are communicated efficiently and acknowledged by all stakeholders, preventing day-of-event chaos.

Key Components of a Communication Plan
A robust communication protocol should be agreed upon at the start of the engagement and outlined in your vendor agreement. Key components include:
Designated Contacts: Clearly identify the primary point of contact for both your organization and the vendor to streamline decision-making and issue resolution.
Preferred Channels: Specify the tools for communication, whether it's email for formal requests, a messaging app for quick updates, or a project management platform for task tracking.
Meeting Cadence: Establish a schedule for regular check-ins (e.g., weekly, bi-weekly) to discuss progress, address concerns, and review performance metrics.
Escalation Path: Define a clear procedure for escalating urgent issues or unresolved problems to ensure they receive prompt attention from the appropriate level of management.
Best Practices Comparison of 9 Vendor Management Strategies
Vendor Management Practice | Implementation Complexity 🔄 | Resource Requirements ⚡ | Expected Outcomes 📊 | Ideal Use Cases 💡 | Key Advantages ⭐ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Comprehensive Vendor Due Diligence | High – multi-stage, detailed assessments | High – requires expertise, time, and tools | Risk reduction, compliance assurance | Initial vendor onboarding, high-risk or critical vendors | Reduces vendor failure risks, ensures standards alignment |
Strategic Vendor Segmentation and Portfolio Management | Moderate to High – requires advanced analysis | Moderate – analytics and maintenance efforts | Optimized resource allocation, strategic partnerships | Managing large vendor base, prioritizing vendor management efforts | Focuses effort on critical vendors, improves cost management |
Robust Contract Management and SLA Framework | Moderate – requires contract expertise and systems | Moderate – contract specialists and monitoring tools | Clear expectations, legal protection | All vendor relationships needing performance and accountability | Sets measurable performance standards, reduces legal risks |
Continuous Performance Monitoring and Scorecarding | Moderate – ongoing data collection and analysis | High – analytics, reporting infrastructure | Proactive issue detection, continuous improvement | Ongoing vendor management, performance improvement initiatives | Provides objective performance data, supports proactive decisions |
Integrated Risk Management and Business Continuity Planning | High – comprehensive risk frameworks and contingency plans | High – continuous monitoring and risk management | Reduced disruptions, regulatory compliance | Vendors critical to operations with high risk exposure | Enables crisis response, protects business continuity |
Cross-Functional Vendor Governance and Communication | Moderate to High – coordination across departments | Moderate to High – time for meetings and governance | Enhanced alignment and oversight | Complex organizations needing multi-stakeholder vendor oversight | Leverages diverse expertise, reduces silos |
Vendor Development and Strategic Partnership Building | High – requires collaboration and investment | High – resources for training and partnership programs | Innovation, improved vendor capabilities | Long-term strategic vendors, innovation-focused partnerships | Drives innovation, strengthens relationships |
Technology-Enabled Vendor Management Platforms | High – technology implementation and integration | High – platform licensing, training, and support | Efficiency gains, enhanced visibility | Organizations seeking automation, large vendor bases | Improves process efficiency, enables data-driven insights |
From Transactional to Transformational: Your Next Steps
Navigating the landscape of supplier relationships can feel complex, but as we've explored, implementing a structured approach is the key to unlocking significant value. The nine vendor management best practices detailed in this guide are not just a checklist; they represent a strategic shift in perspective. Moving from a reactive, transactional model to a proactive, partnership-based framework is what separates thriving businesses from those that merely survive, especially within a dynamic environment like The Ten District.
You've learned the critical importance of starting strong with comprehensive vendor due diligence and the strategic power of segmenting your vendors to focus your energy where it matters most. We've highlighted how a robust contract and SLA framework acts as the foundation for clear expectations, while continuous performance monitoring ensures those expectations are consistently met. This data-driven approach allows you to manage relationships with clarity and confidence.
Turning Best Practices into Business Practice
The journey to mastering vendor management is incremental. It’s about building a sustainable system, not attempting a complete overhaul overnight. The goal is to create a resilient operational backbone for your small business or event planning venture, one that can withstand market shifts and unexpected challenges.
Here are your immediate, actionable next steps:
Conduct a Quick Audit: Review your top five most critical vendors. Are your contracts clear and current? Do you have defined Service Level Agreements? Identifying these initial gaps is a powerful first step.
Pick One Practice to Pilot: Don't feel pressured to implement all nine strategies at once. Choose one that addresses your most pressing pain point. For many, formalizing a performance scorecard or establishing a cross-functional communication channel yields the quickest and most visible returns.
Leverage Simple Tools: You don't need a massive software budget to start. A well-organized spreadsheet can track contracts, performance metrics, and key contacts. As you grow, you can then explore more sophisticated technology-enabled platforms.
Ultimately, embracing these vendor management best practices is about more than just mitigating risk or cutting costs. It is about building a powerful ecosystem of partners who are as invested in your success as you are. When your caterers, suppliers, and service providers become strategic allies, they bring innovation, reliability, and a competitive edge that can't be replicated. This collaborative energy is the force that propels small businesses and memorable events forward, creating a stronger, more interconnected local economy. The effort you invest today in building these foundational practices will pay dividends for years to come, solidifying your reputation and ensuring long-term resilience and growth.
Ready to find your next great local partner? The directory at The Ten District connects you with a curated list of trusted, vetted vendors right here in our community. Start building your strategic partnerships today by exploring the exceptional businesses featured on The Ten District.



Comments